Description
Release form
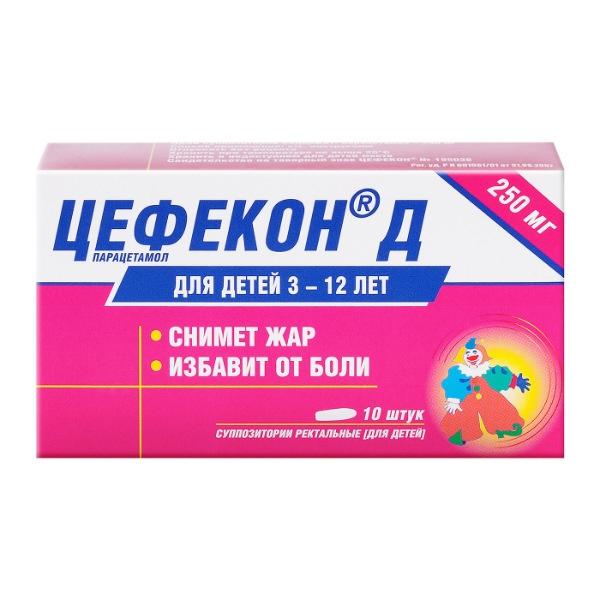
Cefecon ® D rectal suppositories for children of 50 mg, 100 mg or 250 mg. Five suppositories in blister packs two blister packs together with instructions for medical use of the drug are placed in a cardboard box.
Packaging
For 5 suppositories in blister packs, two blister packs together with instructions for medical use of the drug are placed in a cardboard box.
Pharmacological action
Pharmacodynamics:
Paracetamol has analgesic and antipyretic effects. The drug blocks cyclooxygenase in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation. In inflamed tissues, cellular peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on cyclooxygenase, which explains the absence of a significant anti-inflammatory effect.
The absence of a blocking effect on the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues causes it to have a negative effect on water-salt metabolism (sodium and water retention) and the gastrointestinal mucosa.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption is high, rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The period of reaching maximum concentration is 30-60 minutes. Penetrates through the blood-brain barrier. The bioavailability in children and infants is similar to that in adults. Metabolized in the liver. The elimination half-life is 2-3 hours. Within 24 hours, 85-95% of paracetamol is excreted by the kidneys in the form of glucuronides and sulfates, unchanged – 3%. There is no significant age-related difference in the rate of elimination of paracetamol and in the total amount of the drug that is excreted in the urine.
Indications
Used in children from 3 months to 12 years of age as:
antipyretic in acute respiratory infections, flu, childhood infections, post-vaccination reactions and other conditions accompanied by fever
painkiller and mild pain syndrome intensities, including: headache and toothache, muscle pain, neuralgia, pain from injuries and burns.
In children from 1 to 3 months, a single dose of the drug is possible to lower the temperature after vaccination, the use of the drug for all indications is possible only as directed by the doctor.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the components of Cefecon D
age up to 1 month of life.
Caution: impaired liver and kidney function
syndrome Gilbert Dubin-Johnson and Rotor
blood system diseases (anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia)
genetic lack of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Special instructions
If you continue to have fever for more than 3 days and pain for more than 5 days, you should consult your doctor.
The simultaneous use of paracetamol with other paracetamol-containing drugs should be avoided, as this may cause an overdose of paracetamol.
When using the drug for more than 5-7 days, peripheral blood counts and the functional state of the liver should be monitored. Paracetamol distorts the performance of laboratory tests in the quantitative determination of glucose and uric acid in plasma.
Composition
One suppository contains: active substance – paracetamol – 50 mg, 100 mg or 250 mg of the basis for suppositories: solid fat (vitepsol, supposir) – to obtain a suppository weighing 1.25 g
Dosage and administration
Rectally, after a cleansing enema or spontaneous bowel movement. The dosage of Cefecon D is calculated depending on age and body weight, in accordance with the table. The average single dose is 10-15 mg / kg 2-3 times a day after 4-6 hours.
The maximum daily dose of paracetamol should not exceed 60 mg / kg.
1-3 months (4-6 kg) – 1 supp. 50 mg (50 mg)
3-12 months (7-10 kg) – 1 supp. 100 mg (100 mg)
from 1 year to 3 years (11-16 kg) – 1-2 supp. 100 mg (100-200 mg)
from 3 to 10 years (17-30 kg) – 1 supp. 250 mg (250 mg)
from 10 to 12 years (31-35 kg) – 2 supp. 250 mg (500 mg).
Side effects of
From the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain.
Allergic reactions: itching, rash on the skin and mucous membranes, urticaria, Quincke’s edema.
From the hemopoietic organs: anemia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
With prolonged use in large doses, hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects (interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis), hemolytic anemia.
Drug Interactions
Stimulators of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, flumecinol, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants), ethanol and hepatotoxic drugs increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, which makes it possible to develop severe intoxications, even with a slight overdose. Microsomal oxidation inhibitors (including cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity. When taken with salicylates, the nephrotoxic effect of paracetamol increases. The combination with chloramphenicol leads to an increase in the toxic properties of the latter. It enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants, reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
Overdose
Symptoms: during the first 24 hours after administration – pallor of the skin, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain, impaired glucose metabolism, metabolic acidosis. Symptoms of impaired liver function may appear 12-48 hours after an overdose. In severe overdose – liver failure with progressive encephalopathy, coma, death acute renal failure with tubular necrosis (including in the absence of severe liver damage) arrhythmia, pancreatitis. Hepatotoxic effect in adults is manifested when taking 10 g or more.
Treatment: administration of SH-group donors and precursors of glutathione-methionine synthesis 8-9 hours after an overdose and N-acetylcysteine 12 hours later. The need for further therapeutic measures (further administration of methionine, intravenous administration of N-acetylcysteine) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as the time elapsed after its administration.
Storage Conditions
In a dark place at 2-25 ° C.
The Expiration of
is 3 years.
active substance
Paracetamol
lekarstvennaja form
suppozytoryy rektaln e
Prescribed
Children over 3 years old
Indications
Indications
Influenza, From neuritis, From arthrosis and arthritis, Burns, Colds, Migraine
Nizhpharm, Russia