Description
The Latin name
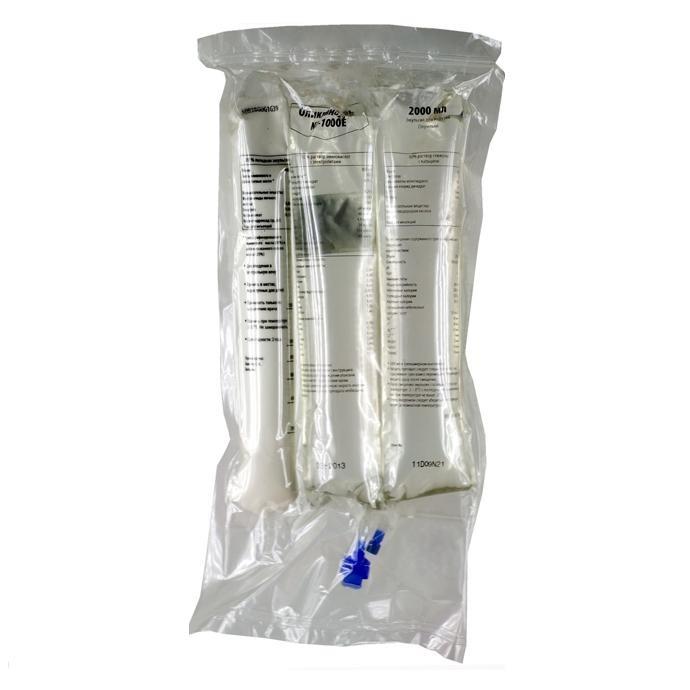
OLICLINOMEL N4-550
Release form
Emulsion for infusion (after mixing the contents of 3 chambers).
Packaging
2 l (800 ml + 800 ml + 400 ml) – three-chamber containers (4) – cardboard boxes.
Indications
Parenteral nutrition in adults and children over 2 years of age in cases where enteral nutrition is impossible, insufficient or contraindicated.
Contraindications
severe renal failure in the absence of hemofiltration or dialysis
severe liver failure
congenital metabolic disorders
severe blood clotting
severe hyperlipidemia srldkrplicm concentration lactic acidosis
pulmonary edema, hyperhydration, decompensated heart failure and hypotonic dehydration
unstable conditions (for example, severe post-traumatic conditions, decompensated diabetes mellitus, acute phase of hypovolemic shock, acute phase of myocardial infarction, severe metabolic acidosis, severe sepsis, hyperosmolar coma)
2 years of age the components of the drug.
Caution: for patients with increased plasma osmolarity, adrenal insufficiency, heart failure, and pulmonary disease.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Currently there are no reliable data on the use of the drug in pregnant and lactating women.
In such cases, the physician must make a decision on his own to assess the ratio of risk and benefit.
Composition of
I chamber – 5.5% solution of amino acids with electrolytes – a clear, colorless or light yellow liquid.
Infusion solution 400 ml
L-alanine 4.56 g
L-arginine 2.53 g
L-histidine 1.27 g
L-isoleucine 1.32 g
L-leucine 1.61 g
hydrochloride) 1.28 g (1.6 g)
L-methionine 880 mg
L-phenylalanine 1.23 g
L-proline 1.5 g
L-serine 1.1 g
L-threonine 920 mg
L-tryptophan 400 mg srdlk90 400 mg srdlk90 mg
L-valine 1.28 g
sodium acetate trihydrate 980 mg
sodium glycerophosphate pentahydrate 2.14 g
potassium chloride 1.19 g
magnesium chloride hexahydrate 450 mg
Excipients: acetic acid – qs water d / i – up to 1 liter.
II chamber – 20% solution of dextrose (glucose) with calcium chloride – a clear, colorless or light yellow liquid.
Infusion solution 400 ml
dextrose (in the form of a monohydrate) 80 g (88 g)
calcium chloride dihydrate 300 mg
Excipients: hydrochloric acid – qs, water d / i – up to 1 l.
III chamber – 10% lipid emulsion – homogeneous white or almost white liquid.
Infusion emulsion 200 ml
a mixture of olive and soybean oils * 20 g
* A mixture of refined olive oil (80%) and soybean oil (20%).
Excipients: purified egg lecithin – 1.2 g, glycerol – 2.25 g, sodium oleate – 30 mg, sodium hydroxide – qs, d / i water – up to 1 liter.
After mixing the contents of three sections, the resulting mixture is a white emulsion and contains:
1 l1.5 l2 l
nitrogen (g) 3.65.47.3
amino acids (g) 223344
total calories (kcal) 6109101215 srldkp non-protein calories (k 5207801040
carbohydrate calories (kcal) 320480640
fat calories (kcal) 200 300 400
non-protein calorie / nitrogen ratio (kcal / g N) 144144144
sodium (mmol) 213242
potassium (mmol) 16p3.3324.3324.33 (mmol) 234
phosphates (mmol) 8.51317
acetates (mmol) 304661
chlorides (mmol) 335066
pH666
osmolarity (mOsmol / l ) 750750750
Dosage and administration of
IV in the central or peripheral vein.
Dose and duration of administration are determined by the need for parenteral nutrition in each individual patient, depending on his condition.
Adults
The average requirement for organic nitrogen is 0.16-0.35 g / kg / day (approximately 1-2 g of amino acids / kg / day).
Energy needs vary depending on the condition of the patient and the intensity of the catabolic processes. On average, they are 25-40 kcal / kg / day.
The maximum daily dose is 40 ml / kg body weight (which is equivalent to 0.88 g of amino acids, 3.2 g of dextrose and 0.8 g of lipids per kg of body weight), i.e. 2800 ml of an emulsion for infusion to a patient having a body weight of 70 kg.
Children over 2 years of age
The average need for organic nitrogen is 0.35-0.45 g / kg / day (approximately 2-3 g of amino acids / kg / day).
Energy needs vary with age, patient condition, and catabolic rate. On average, they are 60-110 kcal / kg / day.
The dose depends on the amount of fluid ingested and the daily requirement of protein. In this case, the state of water metabolism should be taken into account.
The maximum daily dose is 100 ml / kg body weight (which is equivalent to 2.2 g of amino acids, 8 g of dextrose and 2 g of lipids per kg of body weight). As a rule, the dose of 3 g / kg / day of amino acids and / or 17 g / kg / day of dextrose and / or 3 g / kg / day of lipids should not be exceeded, except in special cases.
Maximum infusion rate: the infusion rate should not exceed 3 ml / kg / h, i.e. no more than 0.06 g of amino acids, 0.24 g of dextrose and 0.06 g of lipids per 1 kg of body weight / h.
How to use
A. Opening the package.
1. Break the containment.
2.After opening the containment, discard a bag of oxygen-absorbing substance (if any),
3. Ensure the integrity of the container and the partitions between the chambers.
4. Use only if the container is not damaged and the integrity of the partitions between the chambers is not broken (i.e. the contents of the three chambers were not mixed) while the solutions of amino acids and dextrose should be transparent, and the emulsion should be homogeneous.
B. Mixing of solutions and emulsions.
1. Make sure that the product has an ambient temperature at the time of the destruction of the partitions between the chambers.
2. Manually rotate the top of the container (for which it is suspended) around its axis.
3. The partitions will disappear from the future inlet. Continue twisting the top until the partitions open for at least half their length. Stir by turning the container (at least 3 times).
B. Preparation for infusion.
1. Aseptic conditions must be observed.
2. Suspend the container.
3. Remove the plastic fuse from the future outlet.
4. Attach the infusion system to this place.
G. Concurrent administration of other nutrients.
Any additional nutrients (including vitamins) can be added to the finished mixture.
Vitamins can also be added to the chamber with a dextrose solution before mixing the contents of the chambers.
Oliklinomel can be supplemented with the following components:
– electrolytes: the stability of the emulsion is maintained when adding no more than 150 mmol of sodium, 150 mmol of potassium, 5.6 mmol of magnesium and 5 mmol of calcium / 1 l of the prepared
mixture – organic phosphates: stability of the emulsion is maintained when adding up to 15 mmol / 1 container
– trace elements and vitamins: the stability of the emulsion is maintained when adding doses not exceeding the daily allowance.
Micronutrients should be added under aseptic conditions by injection of micronutrients through a dedicated port.
1. Prepare the container port.
2. Pierce the port and inject the micronutrient solution.
3. Mix the added substances with the contents of the container.
D. Rules for the administration of the drug.
If Oliklinomel was stored at a low temperature, make sure that the drug is warmed to room temperature before using it.
The drug should be administered only after how the integrity of the partitions between all three sections is broken and their contents are mixed.
Side effects
Possible side effects: hyperthermia, sweating, tremors, nausea, headache, respiratory failure.
A temporary increase in the concentration of biochemical markers of liver function (such as alkaline phosphatase, transaminases, bilirubin) was also sometimes observed, especially with prolonged use of parenteral nutrition (several weeks).
In rare cases, hepatomegaly and jaundice developed.
Reduced ability to eliminate lipids contained in oliklinomel from the bloodstream can cause fat overload syndrome, which can be caused by an overdose or occur at the beginning of the infusion, which is accompanied by a sudden deterioration in the patient’s condition. Fat overload syndrome is characterized by hyperlipidemia, fever, fatty liver, hepatomegaly, anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, coagulation disorders and coma. These symptoms are reversible if the infusion of the lipid emulsion is stopped. Rare cases of thrombocytopenia in children who received lipid emulsion infusions have also been reported.
The drug contains soybean oil, which can cause a severe allergic reaction (rarely).
Infusion should be stopped immediately as soon as any symptoms of an allergic reaction appear (such as fever, trembling, skin rash, respiratory failure).
Drug Interaction
The emulsion for infusion should not be administered concurrently with blood products through the same catheter because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination.
If blood sampling was performed before As lipids are eliminated from the plasma (usually 5-6 hours after discontinuation of the emulsion), the lipids contained in the emulsion may affect the results of some laboratory tests, for example, they can change the indices of bilirubin, lactate dehydrogenase, oxygen saturation, hemoglobin.
Overdose
Symptoms: hypervolemia, acidosis, nausea, vomiting, shaking, electrolyte imbalance in case of overdose and / or at an injection rate in excess of the recommended dose. If too high doses of dextrose are administered, hyperglycemia, glucosuria, and hyperosmolar syndrome may develop.
Treatment: In such cases, the infusion should be stopped immediately. Reduced ability to eliminate lipids from the bloodstream can cause fat overload syndrome, all manifestations of which are reversible after discontinuation of the drug.
In severe cases, hemodialysis, hemofiltration or hemodiafiltration may be required
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children at a temperature of 2 ° to 25 ° C. Do not freeze.
After mixing, the emulsion is stable for 7 days from 2 ° to 8 ° C, followed by storage for up to 48 hours at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Do not use after the expiration date indicated on the cardboard box.
Expiration
Expiration is 2 years.
Deystvuyuschee substances
amino acids for parenteral POWER
pharmacy package from
pharmacies Prescription
dosage form
dosage form
infusion solution
Baxter, United States