Description
Release form
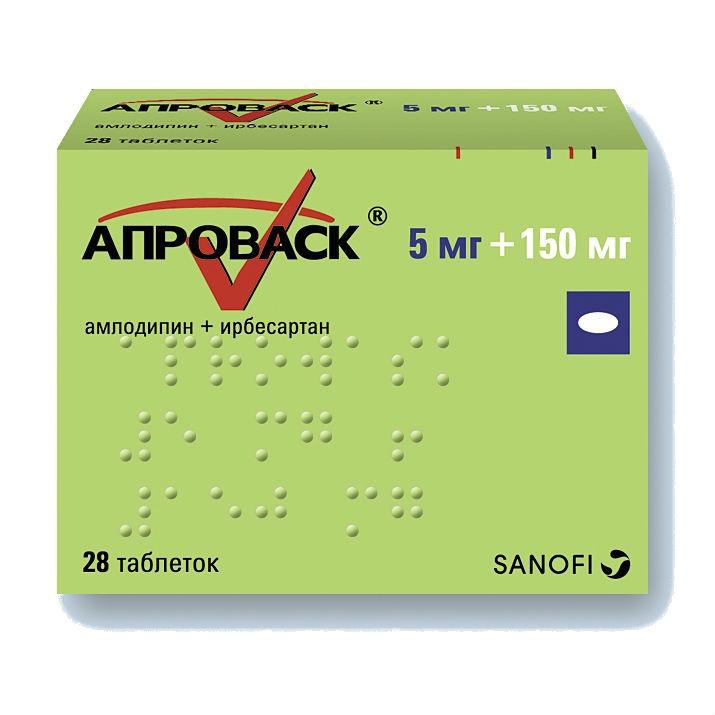
White film coated tablets, oval, biconvex, with engraving 150/5 on one side.
Packaging
7 pcs – blisters (4) – packs of cardboard.
Indications
Arterial hypertension (if monotherapy with irbesartan or amlodipine is not effective).
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to irbesartan, amlodipine and other dihydropyridine derivatives, as well as auxiliary substances of the
preparation cardiogenic shock
clinically significant aortic stenosis
unstable angina (except for Prinzmetal angina)
pregnancy
breastfeeding period
children and adolescents under the age of 18 years (drug efficacy and safety have not been established simultaneously) containing aliskiren in patients with diabetes mellitus or with moderate and severe renal failure (glomerular filtration rate [GFR] <60 ml / min / 1.73 m2 of body surface) simultaneous use with ACE inhibitors in patients with diabetic nephropathy. Precautions: In patients with hypovolemia and hyponatremia that occur, for example, during intensive treatment with diuretics, hemodialysis, following a diet with a limited intake of salt, diarrhea, vomiting. In patients whose renal function depends on RAAS activity (such as patients with arterial hypertension with renal artery stenosis of one or both kidneys, patients with chronic heart failure of functional class III-IV according to NYHA classification), treatment with drugs that affect RAAS , was associated with the development of oliguria and / or progressive azotemia and rarely acute renal failure and / or death, the risk of which cannot be ruled out with ARA II, including irbesartan). In patients with chronic heart failure of the II-IV functional class according to NYHA classification of non-ischemic etiology (due to the content of amlodipine in the preparation, the use of which in such patients was associated with an increase in reports of the development of pulmonary edema compared with placebo, despite the absence of differences in the frequency of progression of heart failure). In patients with liver failure (risk of an increase in T1 / 2 of amlodipine). In patients with renal failure and after kidney transplantation (due to the content of irbesartan in the preparation, it is recommended that potassium and blood creatinine concentration be monitored) after a recent kidney transplant (lack of clinical experience with irbesartan). In patients with aortic and mitral valve stenosis or hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (GOKMP). In patients with coronary heart disease and / or clinically significant cerebral arteriosclerosis (with an excessive decrease in blood pressure there is a risk of increased ischemic disorders, up to the development of acute myocardial infarction and stroke). In patients with SSSU (due to the content of amlodipine in the preparation). Use during pregnancy and lactation There are no sufficient and well-controlled studies of the use of Aprovask ® in pregnant women. Exposure to the fetus of ACE inhibitors taken by pregnant women in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy caused damage and death to the developing fetus. Like any other drugs that directly affect RAAS, Aprovask ® is contraindicated in pregnancy. Aprovask ® should not be used in women of childbearing age who do not use effective methods of contraception. If pregnancy is detected during treatment with Aprovask ®, should stop taking it as soon as possible. Aprovask ® is contraindicated during breastfeeding. In preclinical studies when administered orally to pregnant rats from 0 to 20 days of gestation of irbesartan in doses> 50 mg / kg body weight / day (which, when converted to kg body weight, is approximately equivalent to the maximum recommended dose of irbesartan in humans [MRIH] of 300 mg / day) in rat fetuses, transient effects were observed (slight or moderate expansion of the renal pelvis, hydroureter, and / or absence of the renal papillae). When oral administration of irbesartan in doses of 180 mg / kg body weight / day (approximately equivalent to 4 MRDICH calculated in kg of body weight) in pregnant rats from 0 to 20 days of gestation, the development of subcutaneous edema was observed in rat fetuses. Because these developmental disorders were not observed with limited oral administration of irbesartan at doses of 50, 150 and 450 mg / kg body weight / day to pregnant rats from 6 to 15 days of gestation, they are likely to be late gestational effects of irbesartan. In rabbits, the use of irbesartan at a dose of 30 mg / kg body weight / day was associated with maternal mortality and abortion. Surviving females who received a dose equivalent to 1.5 MRDIC when converted to kg of body weight had a slight increase in fetal resorption and, accordingly, a decrease in the number of live fetuses in the litter. It was found that irbesartan crosses the placental barrier in rats and rabbits. In rats and rabbits, the teratogenic effects of amlodipine were not detected.
Composition
1 tab.
amlodipine besilate 7 mg,
? which corresponds to the content of amlodipine 5 mg
irbesartan 150 mg
Excipients: microcrystalline cellulose 50 μm – 66 mg, croscarmellose sodium – 12 mg, hypromellose 6 mPa.s. colloidal silicon dioxide – 2.5 mg, magnesium stearate – 2.5 mg.
Composition of the film coat: white opadray (hypromellose – 62.5%, titanium dioxide (E171) – 31.25%, macrogol 400 – 6.25%) – 10 mg.
Dosage and administration of
The drug is taken orally. The tablet is swallowed with water. Aprovask ® can be taken both at the same time as eating, and on an empty stomach (i.e., regardless of the time of eating).
Usually, the initial and maintenance dose of Aprovask ® is 1 tablet / day. Aprovask ® should be used in patients who cannot achieve their blood pressure targets with monotherapy with irbesartan or monotherapy with amlodipine, or to continue treatment of patients already taking irbesartan and amlodipine in separate tablets. Doses should be selected individually, first with the use of separate preparations of irbesartan and amlodipine. Doses are selected depending on the reaction of blood pressure to ongoing therapy and the target value of blood pressure. The maximum recommended dose of Aprovask ® is 150 mg / 10 mg or 300 mg / 10 mg per day (due to the fact that the maximum daily dose of amlodipine is 10 mg).
Generally, in elderly patients and in patients with impaired renal function, a dose reduction is not required.
In patients with impaired liver function, Aprovask ® should be used with caution, due to the presence of amlodipine in the composition of the drug.
Side effects
Frequency of adverse events / reactions (AE / HP) reported in clinical trials on the use of a combination of fixed doses of irbesartan and amlodipine (clinical studies of I-ADD, I-COMBINE and I-COMBO), in clinical trials on the use of irbesartan and its post-marketing use, as well as in clinical studies on the use of amlodipine, was determined by the WHO classification as follows: very often ( 10%) often ( 1% and < 10%) infrequently ( 0.1% and <1%) rarely ( 0.01% and <0.1%) very rarely (<0.01%), the frequency is unknown - according to the available data, the frequency of occurrence of AE / NR cannot be estimated. The frequency of HP that was reported in the post-marketing use of the drug was determined as the frequency is unknown, because information about these HP came from spontaneous messages, without indicating the number of patients taking the drug. In clinical trials, compared with fixed-dose combinations of irbesartan / amlodipine with irbesartan or amlodipine monotherapy, the types and frequency of adverse events that occurred during treatment, possibly related to the treatment being studied, were similar to those observed in previous clinical studies or in post-marketing reports with monotherapy with irbesartan and amlodipine. The most common AEs were peripheral edema, mainly associated with amlodipine. Adverse events observed during treatment and possibly related to the study drug in clinical studies of irbesartan / amlodipine (I-ADD, I-COMBINE and I-COMBO) Fixed combination irbesartan / amlodipine General reactions: often, peripheral swelling infrequently – asthenia. On the part of the organ of hearing and labyrinth disorders: infrequently – vertigo. From the cardiovascular system: often – palpitations, orthostatic hypotension infrequently – sinus bradycardia, excessive decrease in blood pressure. From the nervous system: often – dizziness, headache, drowsiness infrequently – paresthesia. From the reproductive system: infrequently – erectile dysfunction. From the respiratory system: infrequently – cough. From the digestive system: often – swelling of the gums infrequently – nausea, pain in the upper abdomen, constipation. From the urinary system: often – proteinuria infrequently – azotemia, hypercreatinemia. From the side of metabolism: infrequently – hyperkalemia. From the musculoskeletal system: infrequently – joint stiffness, arthralgia, myalgia. Adverse events observed with irbesartan in clinical trials (including clinical studies of I-ADD, I-COMBINE and I-COMBO) and its post-marketing use From the immune system: frequency unknown – hypersensitivity reactions (allergic reactions), in including angioedema, urticaria. From the side of metabolism: frequency unknown – hyperkalemia. On the part of the organ of hearing and labyrinth disorders: often – vertigo frequency is unknown – tinnitus. From the nervous system: often – dizziness, headache * infrequently – orthostatic dizziness. * The incidence of headaches in I-ADD, I-COMBINE, and I-COMBO studies has been assessed as infrequent. From the cardiovascular system: infrequently – tachycardia. From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: frequency unknown – leukocytoclastic vasculitis. From the respiratory system: infrequently – cough. From the digestive system: often – nausea / vomiting, pain in the upper abdomen, disorders of the tongue, including dysgeusia (taste perversion), glossodynia (burning sensation and soreness in the tongue), glossitis (inflammation of the tongue) infrequently – diarrhea, dyspepsia, heartburn, frequency is unknown – jaundice, increased liver function tests, hepatitis. From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: infrequently – alopecia. From the musculoskeletal system: frequency unknown – myalgia. From the urinary system: frequency unknown – impaired renal function, including isolated cases of renal failure in patients with risk factors for its development. From the reproductive system: infrequently – erectile dysfunction. General reactions: often – increased fatigue *, swelling infrequently – pain in the chest, frequency unknown – asthenia. * The incidence of increased fatigue in the I-ADD, I-COMBINE, and I-COMBO studies was assessed as infrequent. Injuries, intoxications and complications of manipulation: infrequently – falls. Adverse events observed with amlodipine in clinical trials (including clinical studies of I-ADD, I-COMBINE and I-COMBO) From the hematopoietic system: very rarely – thrombocytopenia. From the side of the immune system: very rarely – allergic reactions, incl. angioedema, urticaria. From the side of metabolism: very rarely – hyperglycemia. Mental disorders: infrequently – insomnia, lability of mood. From the nervous system: often – dizziness, headache *, drowsiness infrequently – hypesthesia, paresthesia, tremors, taste perversions, syncope very rarely – peripheral neuropathy. * The incidence of headaches in I-ADD, I-COMBINE, and I-COMBO studies was assessed as infrequent. From the side of the organ of vision: infrequently – visual disturbances. On the part of the hearing organ and labyrinth disorders: infrequently – ringing in the ears, vertigo. From the cardiovascular system: often – palpitations, hot flashes of skin to the skin, redness of the skin * very rarely – myocardial infarction, cardiac arrhythmias, ventricular tachycardia and atrial fibrillation (atrial fibrillation), vasculitis. * The incidence of reddening of the skin in the I-ADD, I-COMBINE and I-COMBO studies was evaluated as infrequent. From the respiratory system: often – cough infrequently – shortness of breath, rhinitis very rarely – coughing. From the digestive system: often – nausea, abdominal pain, glossodynia, glossitis infrequently – dyspepsia, vomiting, defecation rhythm change, dry mucous membranes of the oral cavity are very rare – pancreatitis, gastritis, gingival hyperplasia, hepatitis, jaundice and increased activity of liver enzymes (mainly associated with cholestasis). From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: often – contact dermatitis infrequently – skin rash, itching, purpura, increased sweating, change in skin pigmentation (appearance of discolored skin areas), alopecia is very rare – erythema multiforme. From the musculoskeletal system: infrequently – arthralgia, muscle cramps, myalgia, back pain. From the urinary system: infrequently – increased frequency of urination, painful urination, nocturia. From the reproductive system: infrequently – impotence, gynecomastia. General reactions: often – fatigue, swelling *, peripheral edema infrequently – chest pain, asthenia, feeling unwell, pain rarely – swelling of the face. * According to I-ADD, I-COMBINE and I-COMBO studies, the incidence of edema is infrequent. Laboratory and instrumental data: infrequently – weight gain, weight loss. overdose Symptoms: no toxicity has been observed with adults receiving irbesartan at doses up to 900 mg / day. Available data for amlodipine suggest that a severe overdose may lead to marked peripheral vasodilation and possibly to the development of reflex tachycardia. The development of a pronounced and prolonged excessive reduction in blood pressure, up to the development of a fatal shock, has been reported. Treatment: The patient should be closely monitored. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive of the body’s vital functions. There is no specific information on the treatment of irbesartan overdose. Suggested measures for overdose with Aprovask ® include gastric lavage. Activation of activated carbon by healthy volunteers immediately after or 2 hours after ingestion of 10 mg of amlodipine showed a slight decrease in the absorption of amlodipine. Due to the fact that amlodipine is characterized by a high degree of binding to blood proteins and irbesartan is not excreted by hemodialysis, it is unlikely that that hemodialysis may be useful in overdose. With severe overdose, active monitoring of cardiac activity and respiration should be initiated. Frequent measurement of BP is needed. A clinically significant decrease in blood pressure due to an overdose of amlodipine requires active maintenance of cardiovascular activity, including the elevation of the limb. BCC and diuresis should be monitored. It may be necessary to introduce vasoconstrictor drugs to restore vascular tone and blood pressure (provided there are no contraindications to their introduction). In / in the introduction of calcium gluconate may be helpful in eliminating the effects of calcium channel blockade. Storage conditions The drug should be stored out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 30 ° C. The Expiration of is 3 years. Active ingredient Amlodipine, Irbesartan Terms of the pharmacy leave Prescription dosage form Dosage form tablets Sanofi-Aventis de Mexico S.A. December SV, Mexico