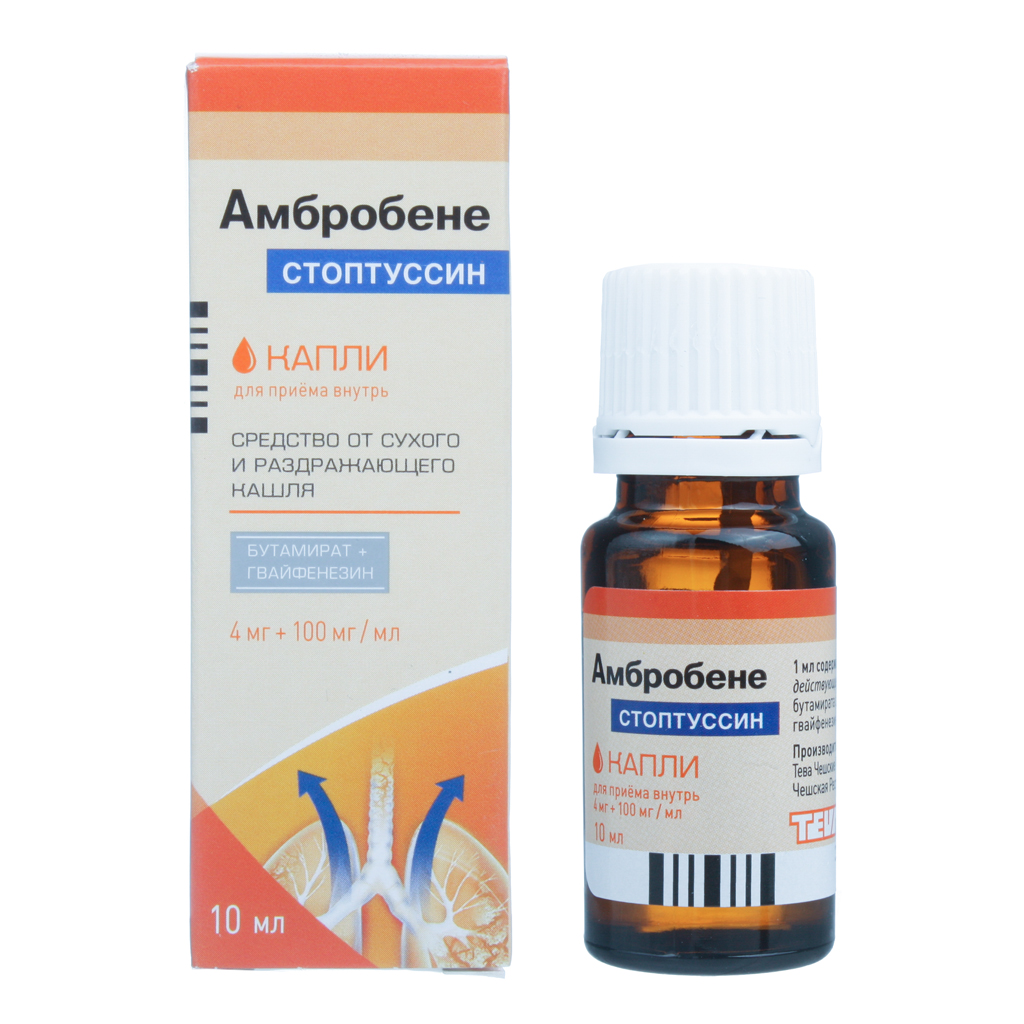
Description
Pharmacological action
Pharmacodynamics
Combined anti-cough and expectorant drug.
Butamirate has a peripheral local anesthetic effect on the sensitive nerve endings of the bronchial mucosa, which provides an antitussive effect.
Guaifenesin increases the secretion of bronchial glands and reduces the viscosity of mucus. Increased secretion is caused both by a direct effect on the bronchial glands – by stimulating the secretion of secretions from the bronchial glands and the removal of acidic glycoproteins from acinar cells, and by the reflex method, when afferent parasympathetic fibers of the gastric mucosa are irritated and the respiratory center is inhibited. Increased tonus of the vagus nerve (n. Vagus) stimulates the production of bronchial secretions. The mucus produced by the bronchial glands enhances the activity of the ciliary epithelium, which facilitates the evacuation of mucus from the bronchi and its coughing.
Pharmacokinetics
When ingested with butamirate, citrate is rapidly and completely absorbed. Communication with plasma proteins is 94%. It undergoes metabolism with the formation of
2 metabolites, which also have an antitussive effect. Metabolites are excreted mainly (90%) by the kidneys and only a small part – through the intestines.
The elimination half-life (T ) is 6 hours.
Guaifenesin, when taken orally, is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Communication with plasma proteins is negligible. Guaifenesin is rapidly metabolized, with the formation of inactive metabolites that are excreted by the kidneys. T – 1 h
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, children under 6 months of age, the first trimester of pregnancy, myasthenia gravis.
With caution
The drug should be used with caution in patients with a tendency to develop drug dependence, with liver disease, alcoholism, epilepsy, brain diseases, as well as in children and pregnant and lactating women.
Use in pregnancy and lactation
There have been no controlled clinical trials of the effect of the drug on pregnant women or animal studies.
When taking guaifenesin in the first trimester of pregnancy, more frequent cases of the formation of an inguinal hernia in the neonatal period were described. The drug should not be taken during the first 3 months of pregnancy. The use of the drug in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy is possible in cases where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
It is not known whether butamirate and guaifenesin pass into breast milk. Due to insufficient information on the use of these drugs during breastfeeding, the risk of side effects in infants cannot be explicitly ruled out. The use of the drug during breastfeeding is possible in cases where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the baby.
Special instructions
Alcoholic beverages are not recommended during treatment with the drug.
If symptoms persist or intensify, seek medical attention.
The drug contains 35.6 vol. % ethanol, the maximum single dose of the drug (40 drops) contains up to 0.322 g of ethanol. This should be considered when prescribing the drug to patients suffering from liver diseases, epilepsy, pregnant and lactating women and children.
The drug should not be prescribed for productive coughing in patients suffering from prolonged or chronic cough (including smoking), bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis, or pulmonary emphysema.
If you missed a drug, do not increase the next dose to compensate for the missed one. If you have questions about taking the drug, contact your doctor.
Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and mechanisms
The drug may have an adverse effect on activities that require increased concentration of attention and speed of psychomotor reactions (for example, driving a car, working with machinery and high-altitude work).
Composition of
1 ml of the preparation contains
active ingredients: guaifenesin 0.100 g, butamirate citrate 0.004 g
excipients 0.3 g 96% , floral fragrance (aroma of alpine flowers) 0.002 g, purified water 0.007 g polysorbate-80 0.001 g, liquorice liquid extract 0.003 g, propylene glycol up to 1,000 ml.
Dosage and administration
The drug is taken after meals, the appropriate number of drops is dissolved in 100 ml of liquid (water, tea, fruit juice, etc.). If a syringe for dosing is attached to the drug, you can use it to accurately set the drug.
Dose depending on the patient ² ¢s body weight:
up to 7 kg, 8 drops 3-4 times a day,
7-12 kg, 9 drops 3-4 times a day,
12-20 kg, 14 drops 3 times a day ,
20-30 kg, 14 drops 3-4 times a day,
30-40 kg, 16 drops 3-4 times a day,
40-50 kg, 25 drops 3 times a day,
50-70 kg 30 drops 3 times a day,
more than 70 kg 40 drops 3 times a day.
If the condition worsens or there is no improvement within 3 days, consult a doctor.
You can use the drug without a doctor ² ¢s prescription for no more than 7 days.
Side effects
Subject to the recommended dosage regimen, patients usually tolerate the drug well. The most commonly reported digestive disorders (nausea, lack of appetite, pain in the stomach, vomiting, diarrhea), headaches, dizziness, and drowsiness, which occur in approximately 1% of patients. These side effects usually decrease after a dose reduction. Skin allergic reactions have also been observed.
The frequency of adverse reactions below was determined according to the following criteria: very often (> 1/10) often (> 1/100 – <1/10) infrequently (> 1/1000 – <1/100) rarely (> 1 / 10000 – <1/1000) is very rare (<1/10000), including individual messages. From the nervous system: often – anorexia, headache. From the side of the organ of hearing and balance: often – dizziness. From the digestive system: often – nausea, pain in the stomach, vomiting, diarrhea. From the skin and subcutaneous fat: very rarely – rashes, urticaria. From the kidneys and urinary tract: very rarely – urolithiasis. In case of any side effects, including effects not listed in the instructions for use, please inform your doctor. Drug interaction Guaifenesin enhances the analgesic effect of paracetamol and acetylsalicylic acid enhances the sedative effect of alcohol, sedatives, hypnotics and general anesthetics on the central nervous system enhances the effect of muscle relaxants. False results may be obtained when determining the concentrations of vanillyl mindal and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid using nitrosonaphthol as a reagent. Therefore, the use of drugs containing guaifenesin should be stopped 48 hours before urine collection for this analysis. Overdose Symptoms: In case of an overdose, signs of toxic effects of guaifenesin prevail: drowsiness, muscle weakness, nausea and vomiting. Perhaps the development of urolithiasis. Treatment: In case of overdose, consult a doctor. Guaifenesin does not have a specific antidote. Prescribe gastric lavage, taking activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy aimed at supporting cardiovascular, respiratory and renal functions, electrolyte balance. Storage conditions In the dark place at a temperature of 10 to 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children. Expiration 5 years. Dosage form drops for ingestion Indications Cough