Description
Latin name
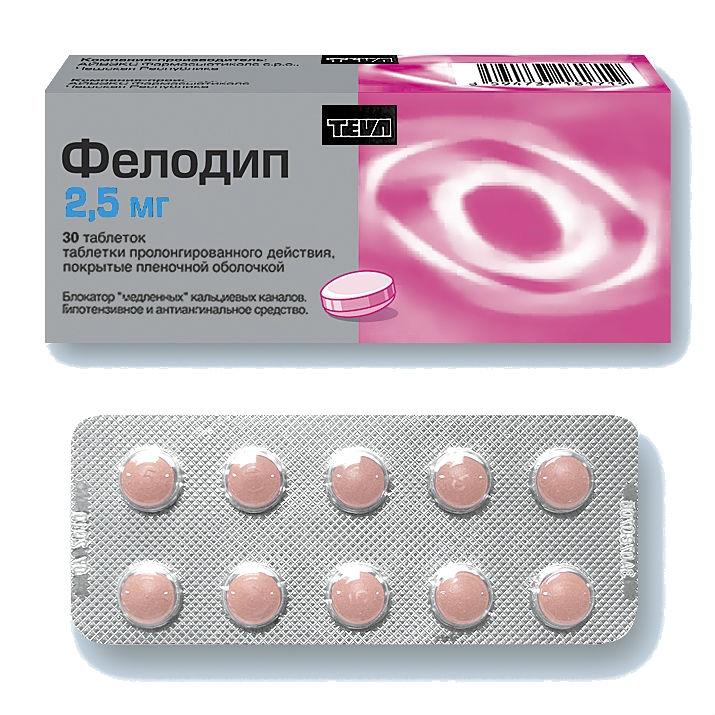
FELODIP
Release form
Long-acting coated tablets.
Packing
30 pcs
Indications
– Arterial hypertension.
– Angina pectoris (including Prinzmetal angina).
Contraindications
– Unstable angina pectoris.
– Acute myocardial infarction and the period up to 1 month after myocardial infarction.
– Cardiogenic shock.
– Clinically significant aortic stenosis.
– Decompensated heart failure.
– Severe arterial hypotension.
– Pregnancy.
– Lactation (breastfeeding).
– Children and adolescents under 18 years of age (efficacy and safety not established).
– Hypersensitivity to the drug or to other derivatives of dihydropyridine.
Use caution with hepatic and / or renal failure.
Special instructions
Felodip (like other vasodilators) can, in rare cases, cause significant arterial hypotension, which in predisposed patients can lead to the development of myocardial ischemia.
There is currently no data on the advisability of using the drug as a secondary prevention of myocardial infarction.
Felodip is effective and well tolerated by patients, regardless of gender and age, as well as patients with bronchial asthma and other obstructive pulmonary diseases, with impaired renal function, diabetes mellitus, with gout, hyperlipidemia, Raynaud’s syndrome, and also after lung transplantation.
Felodip does not affect plasma glucose concentration and lipid profile.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and control mechanisms: patients who experience weakness, dizziness during treatment with Felodip, should refuse to drive vehicles and work, requiring increased attention and concentration.
Composition
1 sustained-release coated tablet contains: felodipine 2.5 mg.
Excipients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, hypromellose, povidone, propyl gallate, magnesium stearate, anhydrous colloidal silicon, iron oxide yellow, iron oxide red, titanium dioxide, talc, propylene glycol.
Dosage and administration
The drug is recommended to be taken in the morning before meals or after a light breakfast. Coated tablets should not be crushed, divided or crushed.
Use for arterial hypertension: the dosage regimen for adults (including the elderly) is set individually. The initial dose is 5 mg 1 time / day (2.5 mg tablets are recommended for dose selection). If necessary, the dose can be increased, the average dose for maintenance therapy is 5-10 mg / day. Felodip can be used in combination with beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors or diuretics, while the hypotensive effect is enhanced (caution should be exercised due to the increased risk of arterial hypotension).
Use in elderly patients or patients with impaired liver function: the initial dose is 2.5 mg / day.
Use in severely impaired liver function: the dose should be reduced.
Application for stable angina pectoris: dose is determined individually. The initial dose for adults is 5 mg 1 time / day, if necessary, increase the dose to 10 mg 1 time / day. The maximum daily dose is 20 mg 1 time / day.
Side effects
The drug (as with other slow calcium channel blockers) can cause facial flushing, headache, palpitations, dizziness, and increased fatigue. These reactions are reversible and most often occur at the beginning of treatment and with an increase in the dose of the drug. Also, depending on the dose, peripheral edema may occur, which is the result of precapillary vasodilation. Patients with gum disease or periodontitis may experience mild gum swelling. This can be prevented by careful oral hygiene.
In some cases: Dermatological reactions: rarely – urticaria, itching in isolated cases – photosensitivity.
From the musculoskeletal system: in isolated cases – arthralgia, myalgia.
From the side of the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system: headache, dizziness in isolated cases – paresthesia.
From the digestive system: rarely – nausea, gingival hyperplasia, increased activity of liver enzymes.
From the cardiovascular system: rarely – palpitations, tachycardia, peripheral edema.
Other: rarely – increased fatigue in isolated cases – hypersensitivity reactions (including angioedema).
Drug Interactions
With simultaneous use with Felodip, the concentration of digoxin in the plasma increases, however, a change in the dosage regimen of Felodip is not required. With simultaneous use with cytochrome P450 inhibitors (including with cimetidine, erythromycin, itraconazole, ketoconazole), felodipine metabolism in the liver slows down, which leads to an increase in its concentration in blood plasma. With the simultaneous use of microsomal liver enzymes with inducers (including with phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampicin, barbiturates), a decrease in the concentration of felodipine in blood plasma occurs. NSAIDs do not weaken the hypotensive effect of Felodip. The high degree of binding of felodipine to plasma proteins does not affect the binding of free fractions of other drugs (including warfarin). Beta-blockers, verapamil, tricyclic antidepressants and diuretics enhance the hypotensive effect of Felodip. Felodip should not be used simultaneously with grapefruit juice because of the flavonoid present in it, which increases the bioavailability of felodipine.
Overdose
Symptoms: marked hypotension, bradycardia.
Treatment: carry out symptomatic therapy. At the expressed arterial hypotension the patient should be given a horizontal position with the legs elevated. In bradycardia – in / in the introduction of atropine at a dose of 0.5-1 mg. If necessary, infusion of glucose, sodium chloride or dextran is carried out to increase the plasma volume. Drugs with a predominant effect on -Adrenoreceptors are prescribed when the above measures are ineffective.
Storage Conditions
Store at 10 ° C to 25 ° C in a dark place.
active substance
Felodipine
Prescription conditions
prescription
Dosage form
tablet prolong.
Teva Pharmaceutical Enterprises Co., Ltd., Israel