Description
Latin name
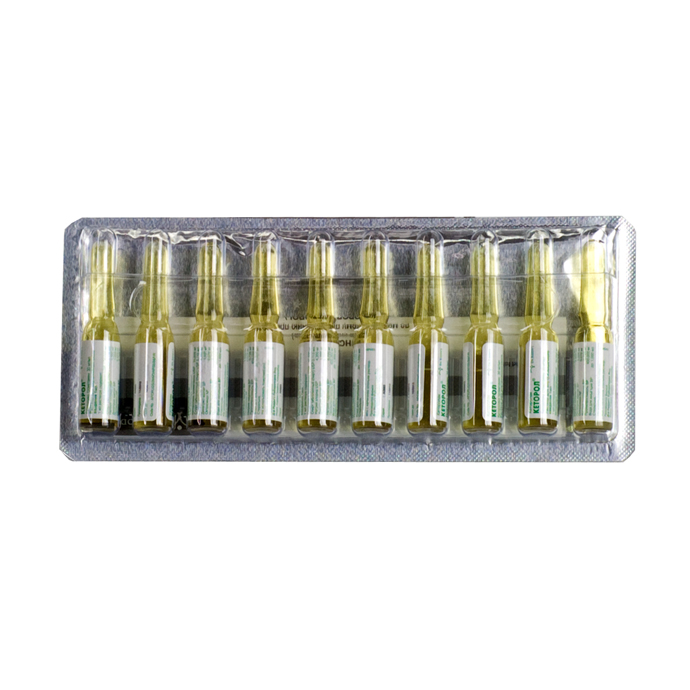
Ketorol
Release form
Solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration
Packing
10 ampoules of 1 ml
Pharmacological action
Pharmacodynamics
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), has a pronounced analgesic effect, has anti-inflammatory and moderate antipyretic effect.
The mechanism of action is associated with non-selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX) activity – COX-1 and COX-2, which catalyzes the formation of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid, which play an important role in the pathogenesis of pain, inflammation and fever.
Ketorolac is a racemic mixture of [-] S and [+] R enantiomers, with the analgesic effect being due to the [-] S form. The strength of the analgesic effect is comparable to morphine, significantly superior to other NSAIDs. The drug does not affect opioid receptors, does not inhibit respiration, does not cause drug dependence, does not have a sedative and anxiolytic effect.
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of ketorolac after single and multiple intravenous and intramuscular administration is linear.
With intramuscular administration, absorption is complete and fast. The maximum concentration of the drug (Cmax) after intramuscular injection of 30 mg is 1.74-3.1 μg / ml, 60 mg is 3.23-5.77 μg / ml, the time to reach the maximum concentration (TCmax) is 15-73 min and 30-60 minutes, respectively. Cmax after intravenous administration of 15 mg – 1.96-2.98 μg / ml, 30 mg – 3.69-5.61 μg / ml, TCmax – 0.4-1.8 min and 1.1-4.7 min, respectively.
Communication with plasma proteins – 99%. The time to reach the equilibrium concentration of the drug (Css) with a parenteral administration of 30 mg 4 times a day is 24 hours with an intramuscular injection of 15 mg is 0.65 1.13 μg / ml, 30 mg is 1.29 2.47 μg / ml .
Distribution volume (Vd) for intramuscular administration – 0.136-0.214 l / kg, for intravenous administration – 0.166-0.254 l / kg. In patients with renal failure, the volume of distribution of the drug may double, and the volume of distribution of its R-enantiomer by 20%.
Penetrates into breast milk: when the mother takes 10 mg of ketorolac, Cmax in milk is reached 2 hours after the first dose and is 7.3 ng / ml, 2 hours after the second dose of ketorolac (when using the drug 4 times a day) – 7.9 ng / l. About 10% of ketorolac passes through the placenta.
More than 50% of the administered dose is metabolized in the liver to form pharmacologically inactive metabolites. The main metabolites are glucuronides, which are excreted by the kidneys, and pharmacologically inactive p-hydroxyketorolac.
It is excreted by 91% by the kidneys, 6% – through the intestines.
The half-life (T1 / 2) in patients with normal renal function is 3.5 9.2 hours after parenteral administration of 30 mg. T1 / 2 increases in elderly patients and shortens in young patients.
Changes in liver function do not affect T1 / 2.
In patients with impaired renal function, with a plasma creatinine concentration of 19-50 mg / l (168-442 mmol / l), T1 / 2 – 10.3-10.8 hours, with more severe renal failure – more than 13, 6 hours
With the introduction of 30 mg of ketorolac intramuscularly, the total clearance is 0.023 l / h / kg (0, 019 l / h / kg in elderly patients) in patients with renal failure (with a plasma creatinine concentration of 19-50 mg / l) – 0.015 l / h / kg. With the introduction of 30 mg of ketorolac intravenously, the total clearance is 0.03 l / h / kg.
Not excreted by hemodialysis.
Indications
Pain syndrome of severe and moderate severity of various origins in injuries, toothache, pain in the postoperative period, with cancer and rheumatic diseases, myalgia, arthralgia, neuralgia, radiculitis.
Intended for symptomatic therapy, reducing pain and inflammation at the time of use. Does not affect the progression of the disease.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to ketorolac
complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose or paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs (including history)
erosive-ulcerative changes in the gastric mucosa and duodenum, active gastrointestinal bleeding, cerebrovascular disease or other bleeding, intestinal disease srdlk , ulcerative colitis) in the exacerbation phase of
hemophilia and other bleeding disorders
decompensated heart failure
liver failure or active the course of liver disease
severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml / min), progressive kidney disease, confirmed hyperkalemia
postoperative period after coronary artery bypass grafting
simultaneous administration with probenecid, pentoxifylline, acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs (including cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors), lithium salts, anticoagulants (including warfarin and heparin)
drug is not used for prophylactic pain relief before and during extensive surgery because of the high risk of bleeding during pregnancy
, lactation period
children under 16 years of age (safety and efficacy not established).
Precautions:
Bronchial asthma, coronary heart disease, congestive heart failure, edema syndrome, arterial hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, pathological dyslipidemia or hyperlipidemia, impaired renal function (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml / l), diabetes mellitus, cholestasis, seps , systemic lupus erythematosus, peripheral artery disease, smoking, old age (over 65 years), anamnestic data on the development of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract,
alcohol abuse, severe somatic diseases, concomitant therapy with the following drugs: antiplatelet agents (e.g. clopidogrel), oral glucocorticosteroids (e.g. prednisone), selective reverse inhibitors serotonin uptake (e.g., citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline).
Special instructions
Ketorol ® has two dosage forms (film-coated tablets and a solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration). The choice of the method of administration of the drug depends on the severity of the pain syndrome and the patient’s condition.
Before prescribing the drug, it is necessary to clarify the issue of a previous allergic reaction to the drug or NSAIDs. Due to the risk of allergic reactions, the first dose is administered under close medical supervision.
Hypovolemia increases the risk of developing nephrotoxic adverse reactions.
If necessary, can be prescribed in combination with narcotic analgesics.
It is not recommended to use as a medicine for prophylactic analgesia, before and during extensive surgery due to the high risk of bleeding. The drug should not be used in conjunction with NSAIDs (including cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors), since when combined with other NSAIDs, fluid retention may occur, decompensation of cardiac activity, increased blood pressure. The effect on platelet aggregation ceases after 24 ² 48 hours.
The drug may alter the properties of platelets.
Patients with impaired blood coagulation are prescribed only with constant monitoring of platelet counts, it is especially important for postoperative patients requiring careful monitoring of hemostasis.
The risk of drug complications increases with prolonged treatment (in patients with chronic pain) and an increase in the dose of the drug more than 90 mg / day.
To reduce the risk of adverse events, the minimum effective dose should be applied with the lowest possible short course.
Misoprostol, omeprazole are prescribed to reduce the risk of developing NSAIDs.
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration of attention and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Composition of
1 ml of the solution contains:
active ingredient:
ketorolac tromethamine (ketorolac trometamol) 30 mg
excipients: octoxynol 0.07 mg,
disodium edetate 1 mg,
ml sodium chloride 4 mg 0.1 ml ,
propylene glycol 400 mg,
sodium hydroxide 0.725 mg,
water for injection up to 1 ml.
Dosage and administration of
Intravenously, intramuscularly.
Ketorol ® solution is used in minimally effective doses, selected in accordance with the intensity of the pain. If necessary, you can simultaneously prescribe narcotic analgesics in reduced doses.
For parenteral administration, to patients from 16 to 64 years old with a body weight exceeding 50 kg, no more than 60 mg is administered intramuscularly once (taking into account oral administration). Usually – 30 mg every 6 hours intravenously? 30 mg each (no more than 6 doses in 2 days).
Intramuscularly, adult patients weighing less than 50 kg or with chronic renal failure (CRF) are given once no more than 30 mg (taking oral administration), usually 15 mg (no more than 8 doses in 2 days) intravenously – no more than 15 mg every 6 hours (no more than 8 doses in 2 days).
The maximum daily doses for intramuscular and intravenous administration are for patients from 16 to 64 years old with a body weight exceeding 50 kg – 90 mg / day for adult patients weighing less than 50 kg or with chronic renal failure, as well as elderly patients (over 65 years old) ) – for intramuscular and intravenous administration of 60 mg. The duration of treatment should not exceed 2 days.
For intravenous administration, the dose must be administered in at least 15 seconds.
Intramuscular injection is carried out slowly, deep into the muscle. The onset of analgesic action is noted after 30 minutes, the maximum analgesia occurs after 1-2 hours.
The analgesic effect lasts about 4-6 hours.
Side effects
The frequency of side effects is classified according to the frequency of occurrence of the case: often (1-10%), sometimes (0.1-1%), rarely (0.01-0.1%), very rarely (less 0.01%), including individual messages.
From the digestive system: often (especially in elderly patients over 65, having a history of erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract) – gastralgia, diarrhea less often – stomatitis, flatulence, constipation, vomiting, a feeling of full stomach rarely – nausea, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (including with perforation and / or bleeding – abdominal pain, spasm or burning in the epigastric region, melena, vomiting like coffee grounds, nausea, heartburn and others), cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, hepatomegaly, acute pancreatitis.
From the urinary system: rarely – acute renal failure, lower back pain with or without hematuria and / or azotemia, hemolytic uremic syndrome (hemolytic anemia, renal failure, thrombocytopenia, purpura), frequent urination, increased or decreased urine volume, nephritis , edema of renal origin.
On the part of the sensory organs: rarely – hearing loss, tinnitus, visual impairment (including blurred visual perception).
From the respiratory system: rarely – bronchospasm, rhinitis, laryngeal edema (shortness of breath, shortness of breath).
From the central nervous system: often – headache, dizziness, drowsiness, rarely – aseptic meningitis (fever, severe headache, cramps, stiff neck and / or back muscles), hyperactivity (mood changes, anxiety), hallucinations, depression, psychosis .
From the cardiovascular system: less often – increased blood pressure rarely – pulmonary edema, fainting.
From the hemopoietic organs: rarely – anemia, eosinophilia, leukopenia.
From the hemostatic system: rarely – bleeding from a postoperative wound, nosebleeds, rectal bleeding.
From the skin: less often – a skin rash (including maculopapular rash), purpura rarely – exfoliative dermatitis (fever with chills or without, redness, tightening or peeling of the skin, swelling and / or tenderness of the tonsils), urticaria, Stevens syndrome – Johnson’s Lyell Syndrome.
Local reactions: less often – burning or pain at the injection site.
Allergic reactions: rarely – anaphylaxis or anaphylactoid reactions (discoloration of the face, skin rash, urticaria, itching, shortness of breath, swelling of the eyelids, periorbital edema, shortness of breath, heaviness in the chest, wheezing).
Other: often – swelling (face, legs, ankles, fingers, feet, weight gain) less often – excessive sweating rarely – swelling of the tongue, fever.
Drug Interactions
The simultaneous use of ketorolac with acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs, calcium, GCS, ethanol, corticotropin can lead to the formation of gastrointestinal ulcers and the development of gastrointestinal bleeding.
The drug should not be used concomitantly with other NSAIDs.
Co-administration with paracetamol increases nephrotoxicity, with methotrexate – hepato- and nephrotoxicity.
The simultaneous administration of ketorolac and methotrexate is possible only when using low doses of the latter (it is necessary to control the concentration of methotrexate in blood plasma).
Probenecid reduces the plasma clearance and Vd of Ketorolac, increases its concentration in blood plasma and increases T1 / 2.
With the use of ketorolac, a decrease in the clearance of methotrexate and lithium and an increase in the toxicity of these substances are possible.
Concomitant use with indirect anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, cefoperazone, cefotetan and pentoxifylline increases the risk of bleeding.
Reduces the effect of antihypertensive and diuretic drugs (decreases the synthesis of PG in the kidneys).
When combined with narcotic analgesics, the doses of the latter can be significantly reduced.
Antacids do not affect the absorption of the drug.
Increases the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs (dose recalculation required).
Co-administration with valproic acid causes impaired platelet aggregation.
Increases the plasma concentration of verapamil and nifedipine.
When prescribed with other nephrotoxic drugs (including gold preparations), the risk of developing nephrotoxicity is increased. Drugs that block tubular secretion reduce the clearance of ketorolac and increase its concentration in blood plasma.
Overdose
Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, impaired renal function, metabolic acidosis.
Treatment: gastric lavage, introduction of adsorbents (activated charcoal) and symptomatic therapy (maintenance of vital functions of the body). It is not adequately eliminated by dialysis.
Storage Conditions
In a dark place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Do not freeze.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children!
shelf life
3 years
Deystvuyushtee substance
Ketorolac
Terms and conditions
prescription
Dosage form
solution for injection and infusion
Possible product names
KETOROL 0.03 / 1ML N10 AMP
KETOROL 0.03 / ML 1ML N10 AMP R-V V / V / M
KETOROL 0.03 / ML 1ML R 10 AMP R-AMP W / M
Ketorol 1ml No. 10 amp
KETOROL 30MG / 1ML. 1ML. RR D / IN. No. 10 AMP.