Description
Description
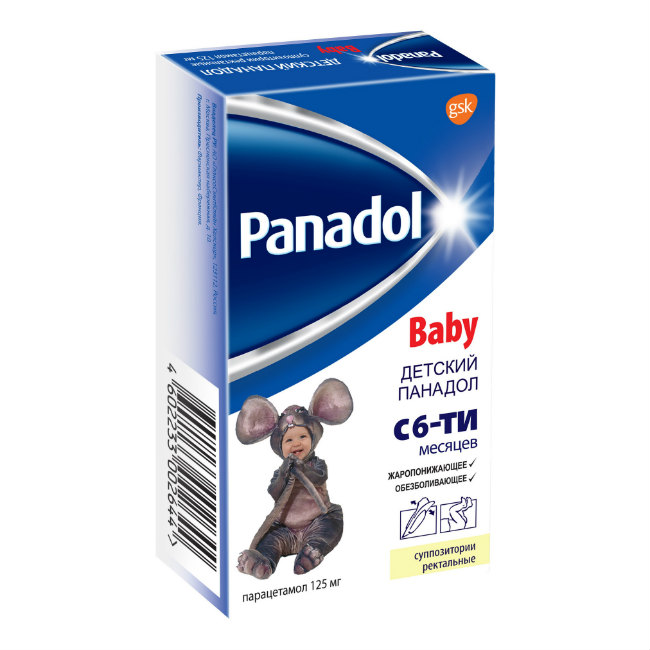
Suppositories rectal white or almost white, cone-shaped, fatty, cone-shaped, fat-like, conical.
Pharmacological action
The drug has analgesic and antipyretic properties.
Blocks cyclooxygenase in the central nervous system by acting on pain and thermoregulation centers.
There is virtually no anti-inflammatory effect.
Does not affect the condition of the gastrointestinal mucosa and water-salt metabolism, since it does not affect the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
Indications
Used in children from 1 year to 9 years (with a body weight of 9 to 31 kg) as:
– an antipyretic to reduce fever in colds, flu and childhood infectious diseases (chickenpox, rubella, whooping cough, measles, scarlet fever, mumps (mumps), etc.)
is an analgesic for teething pains, toothache, ear pain for otitis media and pain in throat.
Pediatric Panadol is recommended to reduce elevated body temperature in children after vaccination.
Contraindications
Child Panadol is not recommended for patients taking
for:
– hypersensitivity to paracetamol or any other component of
– impaired liver and kidney function
– blood disease
– recent inflammation or associated with the route of administration)
– the genetic absence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
– while taking other paracetamol-containing drugs, drugs to relieve the symptoms of the common cold and flu, painkillers and antipyretic drugs for children under 1 year old.
Use with caution in case of impaired liver or kidney function, in Gilbert syndrome. If you have any of these diseases, you should consult your doctor before taking the drug.
Special instructions
Children’s Panadol rectal suppositories are indicated for children who have difficulty taking tablets or are prone to emetics.
When conducting tests to determine uric acid and blood sugar, tell your doctor about the use of the drug Children’s Panadol.
When taking the drug for more than 7 days, monitoring of peripheral blood and the functional state of the liver is recommended.
Glutathione deficiency due to eating disorders, cystic fibrosis, HIV infection, starvation, and malnutrition makes it possible to develop severe liver damage with small overdoses of paracetamol (5 g or more).
The drug should not be used concomitantly with other paracetamol-containing drugs.
Composition
Composition (per suppository):
Active ingredient:
paracetamol 125 mg.
Excipients:
solid fat (SuppocireK AM) 890 mg.
Dosage and administration
The drug is administered rectally. Wash your hands and release the suppository from the plastic shell. Carefully insert the suppository with your index finger into the anus of the child (preferably after a cleansing enema or spontaneous bowel movement). It will be easier to enter when the child is on the left side with one leg pulled up to the stomach.
The average single dose of the drug for children Panadol depends on the body weight of the child and is 10-15 mg / kg body weight 3-4 times a day every 4-6 hours. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 60 mg / kg body weight.
Children with a body weight of 8 to 12.5 kg (usually from 6 months to 2.5 years) are given 1 suppository (125 mg) 3-4 times a day after 4-6 hours. Do not use more than 4 suppositories per day.
Duration of use without consulting a doctor is 3 days.
Do not exceed the recommended dose!
If you accidentally exceed the recommended dose, you should immediately consult a doctor, even if the child is feeling well, as there is a risk of developing liver damage (see Overdose).
If the child s condition does not improve when taking the drug, consult your doctor.
Side effects of
At recommended doses, the drug is usually well tolerated. The following side effects were detected spontaneously during the post-registration use of the drug.
Side effects are classified by organ system and frequency. The frequency of side effects is defined as follows: very often (greater than or equal to 1/10), often (greater than or equal to 1/100 and less than 1/10), infrequently (greater than or equal to 1/1000 and less than 1/100), rarely ( greater than or equal to 1/10 000 and less than 1/1000) and very rarely (greater than or equal to 1/100 000 and less than 1/10 000).
Allergic reactions:
– very rarely – in the form of skin rashes, itching, urticaria, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylaxis
– from the hematopoietic system:
– very rarely – thrombocytopenia, anemia, leukopenia
from the respiratory system rarely – bronchospasm (in patients with hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
From the hepatobiliary system:
– very rarely – impaired liver function.
– nausea, vomiting are sometimes possible.
If any of the following side effects occur, stop taking the drug and consult a doctor immediately.
Drug Interactions
If a child is already taking other drugs, Panadol should be consulted with a doctor before taking the drug.
Barbiturates, carbamazepine, phenytoin, diphenin, primidone and other anticonvulsants, ethanol, rifampicin, zidovudine, flumecinol, phenylbutazone, butadione, St. John’s wort preparations and other microsomal oxidation inducers increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, making it possible to develop severe liver damage with small overdoses of paracetamol (5 g or more).
Inhibitors of microsomal liver enzymes reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Under the influence of paracetamol, the excretion time of chloramphenicol (chloramphenicol) increases by 5 times, resulting in an increased risk of poisoning with chloramphenicol (chloramphenicol).
When taken regularly for a long time, the drug enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin and other coumarins), which increases the risk of bleeding.
Occasionally taking a single dose of the drug does not significantly affect the effect of indirect anticoagulants.
Metoclopramide and domperidone increase, and colestyramine decreases the rate of absorption of paracetamol. The drug may decrease the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
overdose
Symptoms: within the first 24 hours after overdose – nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, sweating, paleness of the skin, anorexia. After 1-2 days, the signs of liver damage (pain in the liver, increased activity of liver enzymes) are determined.
Carbohydrate metabolism and metabolic acidosis may develop.
In adult patients, liver damage develops after taking more than 10 g of paracetamol, in children – when receiving more than 125 mg / kg of body weight of the child. In the presence of factors, affecting the toxicity of paracetamol for the liver, (see section Interaction with other medicines, special instructions) liver damage is possible after taking 5 or more grams of paracetamol.
In severe cases of overdose as a result of hepatic failure can develop encephalopathy (impaired brain function), bleeding, hypoglycemia, brain edema, up to death. The development of acute renal failure with acute tubular necrosis, characteristic of which is pain in the lumbar region, hematuria (impurity of blood or red blood cells in the urine), proteinuria (increased protein content in the urine), with severe liver damage may be absent.
There were cases of cardiac arrhythmias, pancreatitis.
Hepatotoxic and nephrotoxic effects (renal colic, nonspecific bacteriuria, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis) may be observed with prolonged use with excess of the recommended dose.
Treatment: In case of suspected overdose, even in the absence of pronounced first symptoms, it is necessary to discontinue the drug and seek immediate medical attention. With overdosage caused by the administration of paracetamol rectally, gastric lavage and enterosorbents are ineffective. Paracetamol blood plasma levels should be determined, but not earlier than 4 hours after overdose (earlier results are unreliable). Acetylcysteine administration within 24 hours after overdose.
The maximum protective effect is provided within the first 8 hours after overdose, over time, the effectiveness of the antidote drops sharply. If necessary, acetylcysteine is administered intravenously. In the absence of vomiting before the patient’s admission to the hospital, the use of methionine is possible. The need for additional therapeutic measures (further administration of methionine, in / in the introduction of acetylcysteine) is determined by the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as by the time elapsed after its administration.
Treatment of patients with severe hepatic impairment 24 hours after taking acetaminophen should be performed in conjunction with a specialist at the toxicology center or specialist liver disease department.
Storage conditions
Do not store above 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Shelf life
5 years.
Active ingredient
Paracetamol
Terms and conditions
without prescription
dosage form
rectal suppositories
Appointment
Appointment
For children over 6 months old
GlaxoSmithKline, UK