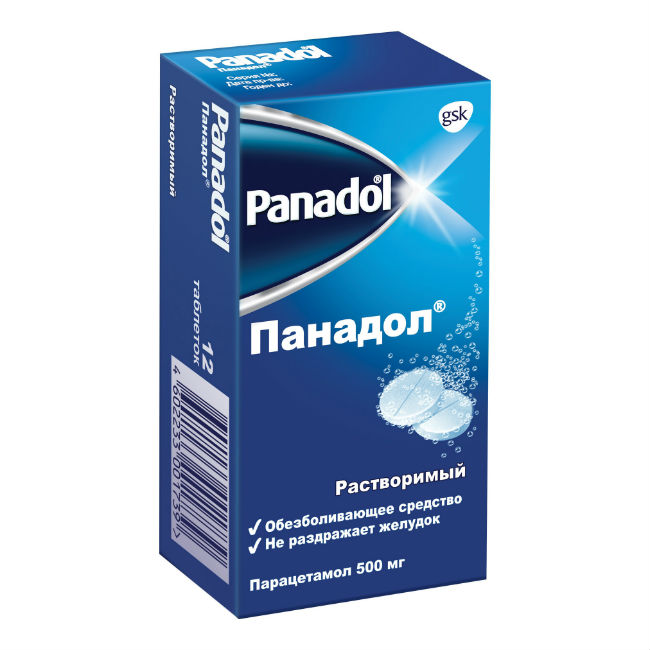
Description
Briefly about the product
Panadol is an analgesic that does not irritate the stomach and intestines. *
Used to relieve
headache srdlkrp sore pain sore pain srdlkrp sdlj pain muscle pain
painful menstruation
Panadol ® is also used for the symptomatic treatment of febrile syndrome (as an antipyretic agent) at elevated body temperature against a background of colds and flu *.
* Instructions for medical use, RU Ñ N014409 / 01
Description
Flat white tablets with a beveled edge, with a risk on one side.
The surface on both sides of the tablet may be slightly rough.
Latin name
Panadol
Release form
2 tablets per laminated strip (kraft bleached paper / poly ethylene / aluminum foil / polyethylene or glass coated paper / polyethylene / aluminum foil / surlin).
6 strips of 2 tablets with instructions for use in a cardboard box.
Pharmacological action
The drug has analgesic and antipyretic properties. It blocks COX1 and COX2 mainly in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation.
There is virtually no anti-inflammatory effect.
Does not irritate the stomach and intestines.
Does not affect water-salt metabolism, since it does not affect the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
Indications
Panadol ® is used to relieve headache, migraine, toothache, sore throat, lower back pain, muscle pain, painful menstruation.
“Panadol ®” is also used for the symptomatic treatment of febrile syndrome (as an antipyretic agent) at elevated body temperature against the background of “colds” and flu.
The drug is intended to reduce pain at the time of use and does not affect the progression of the disease.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to children under 6 years of age.
Use with caution in kidney and liver failure, benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert syndrome), viral hepatitis, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, alcoholic liver damage, alcoholism, in old age.
Use in pregnancy and lactation
According to epidemiological studies in pregnant women, paracetamol does not have adverse effects when used at the recommended doses during pregnancy.
However, use during pregnancy is only possible after consultation with a doctor.
Paracetamol passes into breast milk in an insignificant amount. According to published data, the use during breastfeeding is not contraindicated.
Special instructions
Before taking Panadol ®, you should consult your doctor if you are taking any of the drugs listed in the Interaction with Other Medicines section.
If, while taking the drug, no improvement is observed or the headache becomes constant, consult a doctor.
Glutathione deficiency due to eating disorders, cystic fibrosis, HIV infection, starvation, and malnutrition makes it possible to develop severe liver damage with small overdoses of paracetamol (5 g or more).
The drug should not be taken concomitantly with other paracetamol-containing drugs.
Patients on a salt-free or low-salt diet, when calculating the daily intake of salt, the sodium content in the tablet (427 mg) should be taken into account.
When conducting tests to determine uric acid and blood glucose, you should tell your doctor about taking the drug.
The drug should be used with caution in case of fructose intolerance, since the drug contains sorbitol.
To avoid the toxic effects of liver damage, paracetamol SHOULD NOT BE COMBINED WITH ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES, AND ALSO TAKE PERSONS THEREOUS WITH A CHRONIC CONSUMPTION OF ALCOHOL.
When sodium bicarbonate is consumed in high doses, gastrointestinal disorders may develop, including belching, nausea, hypernatremia may also develop, In this case, it is necessary to control the water-electrolyte balance and apply the appropriate tactics of patient management
Composition
1 tablet contains
Active ingredient
paracetamol 500 mg
Excipients:
sorbitol,
sodium saccharinate,
sodium bicarbonate,
sodium lauric acid,
sodium citric acid
Dosage and Administration
Inside.
“Panadol ®”, soluble tablets, before administration should be dissolved in at least 100 ml (half a glass) of water.
Adults (including the elderly): 1-2
tablets (0.5 to 1 g) up to 4 times daily, as needed. The maximum single dose is 2 tablets (1 g). The maximum daily dose is 8 tablets (4 g). The interval between doses is at least 4 hours.
Children
The dose is calculated based on the body weight of the child: the maximum single dose is 15 mg / kg body weight, the maximum daily dose is 60 mg / kg body weight.
Children (6-9 years old): 1/2 tablet (250 mg) up to 4 times a day, as needed. The maximum single dose is 1/2 tablet (250 mg). The maximum daily allowance is 2 tablets (1 g). The interval between doses is at least 4 hours.
Children (9-12 years): 1 tablet (500 mg) up to 4 times a day, as needed. The maximum single dose is 1 tablet (500 mg). The maximum daily dose is 4 tablets (2 g). The interval between doses is at least 4 hours.
In adults, it is not recommended to use the drug for more than 5 days as an anesthetic and more than 3 days as an antipyretic without the appointment and supervision of a doctor.
In children, the drug is not recommended for use for more than 3 days without the appointment and supervision of a doctor.
Do not exceed the indicated dose. If you exceed the recommended dose, consult a doctor immediately, even if you feel good, since there is a risk of delayed serious liver damage.
An increase in the daily dose of the drug or the duration of treatment is possible only under the supervision of a doctor.
Side effects
At recommended doses, the drug is usually well tolerated. Belowthese side effects were identified spontaneously during the post-registration use of the drug.
Side effects are classified by organ systems and frequency. The frequency of side effects is defined as follows: very often (greater than or equal to 1/10), often (greater than or equal to 1/100 and less than 1/10), infrequently (greater than or equal to 1/1000 and less than 1/100), rarely ( greater than or equal to 1 / 10,000 and less than 1 / 1,000) and very rare (greater than or equal to 1 / 10,000 and less than 1 / 10,000).
Allergic reactions:
Very rare – in the form of rashes on the skin, itching, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylaxis
From the hematopoietic system:
Very rarely – thrombocytopenia, methemoglobinemia, hemoglobinemia
Very rare – bronchospasm (in patients with hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs)
From the hepatobiliary system:
Very rare – impaired liver function.
With prolonged use at high doses, the likelihood of impaired liver and kidney function (renal colic, nonspecific bacteriuria, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis) increases, blood flow monitoring is required.
If any of these side effects occur, stop taking the medication and consult your doctor immediately.
Drug Interaction
Prolonged co-administration of paracetamol and NSAIDs increases the risk of analgesic nephropathy and renal papillary necrosis and the onset of end-stage renal failure.
Concomitant long-term use of paracetamol in high doses and salicylates increases the risk of kidney or bladder cancer.
With regular intake for a long time, the drug increases the effect of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin and other coumarins), which increases the risk of bleeding. Episodic intake of a single dose of the drug has no significant effect on the effect of indirect anticoagulants.
Diflunisal increases the plasma concentration of paracetamol by 50%, which increases the risk of hepatotoxicity. Barbiturates, carbamazepine, phenytoin, primidone, ethanol, rifampicin, zidovudine, flumecinol, phenylbutazone, St. John’s wort drugs, tricyclic antidepressants and other inducers of microsomal oxidation increase the production of hydroxylated peroxidation, ).
Inhibitors of microsomal liver enzymes (cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxic action. Under the action of paracetamol, the elimination time of chloramphenicol is increased 5-fold. Concomitant use of paracetamol and alcoholic beverages increases the risk of liver damage and acute pancreatitis. Metoclopramide and domperidone increase, and cholestyramine reduces the absorption rate of paracetamol. The drug may reduce the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
Storage conditions
Do not store above 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
Expiration
4 years.
active substance
Paracetamol
GlaksoSmithKline, United Kingdom