Description
Latin name
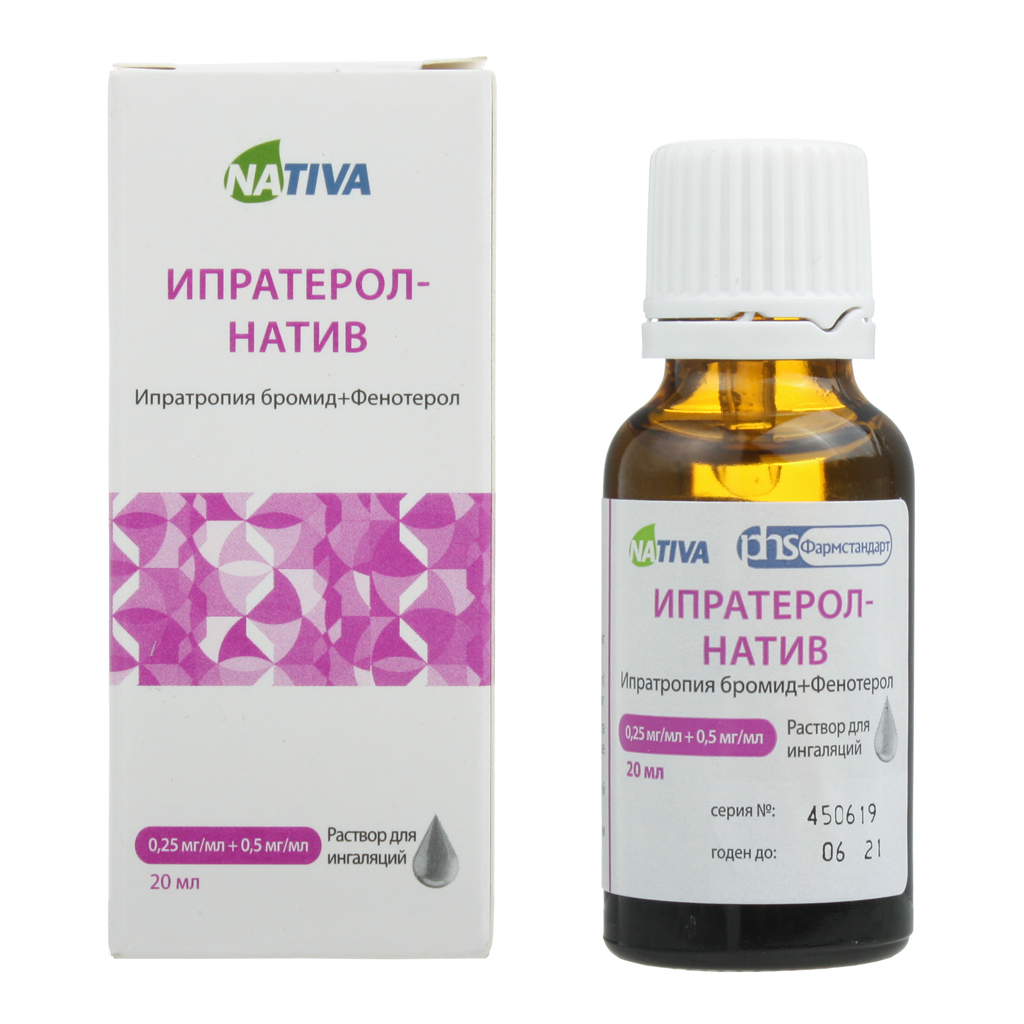
IPRATEROL-nATIV
Release form
Solution for inhalation
Packing
Bottle of 20 ml
Indications
Prevention and symptomatic treatment of chronic obstructive airways diseases with reversible airway obstruction, such as bronchial asthma and especially chronicYes, obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic obstructive bronchitis with or without emphysema.
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to phenoterol or atropine-like drugs or other components of the drug ipraterol native
hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
tachyarrhythmia
I and III trimesters of pregnancy.
Precautions: angle-closure glaucoma, arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, recent myocardial infarction (within the last 3 months), diseases of the heart and blood vessels, such as chronic heart failure, coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, severe lesions of the cerebral and peripheral arteries, hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma, prostatic hyperplasia, obstruction of the bladder neck, cystic fibrosis, II trimester of pregnancy, breastfeeding, children under 6 years old.
Pregnancy and lactation
Preclinical studies and experience with the combination of ipratropium bromide and phenoterol show that the components of the drug do not have a negative effect on pregnancy. The possibility of the inhibitory effect of phenoterol on uterine contractility should be considered. The drug is contraindicated in the I and III trimesters of pregnancy (the possibility of weakening labor by phenoterol). Use with caution in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Fenoterol passes into breast milk. No evidence has been obtained that ipratropium bromide passes into breast milk. However, the drug Ipraterolum should be prescribed with caution to nursing mothers.
Composition of
1 ml of solution contains:
Active ingredient:
ipratropium bromide monohydrate
Excipients:
sodium benzoate 0.5 mg,
disodium edetate 0.5 mg,
1.5 mg citric acid hydrohydrate monohydrate pH 3.2 mg water and up to 1 ml.
Dosing and Administration
Dose should be selected individually. During therapy, medical supervision is required. The following doses are recommended:
In adults (including the elderly) and adolescents over 12 years old:
Acute asthma attacks
In many cases of mild to moderate seizures, 1 ml (20 drops) is recommended. In especially severe cases, for example in patients, located in intensive care units, with the ineffectiveness of the doses indicated above, higher doses may be required, up to 2.5 ml (50 drops). The maximum dose may reach 4.0 ml (80 drops). The maximum daily dose is 8.0 ml (160 drops).
Course and long-term treatment of
If necessary, re-use for each injection use 1-2 ml (20-40 drops) up to 4 times a day.
In case of moderate bronchospasm or as an adjuvant in the exercise of ventilation of the lungs, a dose with a lower level of 0.5 ml (10 drops) is recommended.
In children aged 6-12 years:
Acute asthma attacks
In many cases, 0.5 – 1 ml (10 -20 drops) are recommended for quick relief of symptoms.
In severe cases, if a dose of 1 ml (20 drops) is ineffective, higher doses may be required, up to 2 ml (40 drops).
In especially severe cases, if a dose of up to 2.0 ml (40 drops) is ineffective, it is possible to use (subject to medical supervision) a maximum dose reaching 3.0 ml (60 drops).
The maximum daily dose can reach 4.0 ml (80 drops).
Course and long-term treatment
If necessary, re-use for each administration 0.5 – 1 ml (10-20 drops) up to 4 times a day.
In cases of moderate bronchospasm or as an adjuvant in ventilating the lungs, the recommended dose is 0.5 ml (10 drops).
In children under the age of 6 (whose body weight is less than 22 kg):
Due to that information on the use of the drug in this age group is limited, it is recommended to use the following dose (only subject to medical supervision): about 25 μg ipratropium bromide and 50 μg phenoterol hydrobromide = 0.1 ml (2 drops) per kg body weight (per dose ), but not more than 0.5 ml (10 drops) (per dose). The maximum daily dose is 1.5 ml.
Inhalation solution should be used only for inhalation (with a suitable nebulizer) and do not use oral solution.
Treatment should usually begin with the lowest recommended dose. The recommended dose should be diluted with 0.9% sodium chloride solution to a final volume of 3-4 ml, and be applied (completely) using a nebulizer. Ipraterolum-native solution for inhalation should not be diluted with distilled water.
Dilution of the solution should be carried out every time before use, the remains of the diluted solution should be destroyed.
The diluted solution should be used immediately after preparation.
Dosage may depend on the method of inhalation and the type of nebulizer.
The duration of inhalation can be controlled by spending the diluted volume.
Ipraterolum-native solution for inhalation can be used using various commercial nebulizer models. In cases where there is wall oxygen, the solution is best used at a flow rate of 6-8 liters per minute. Follow the instructions for use, maintenance and cleaning of the device, which is supplied with the nebulizer.
Side effects
From the nervous system: often – small tremor of skeletal muscle, nervousness rarely – headache, dizziness, very rarely – mental change.
From the cardiovascular system: often – tachycardia, including supraventricular tachycardia, palpitations (especially in patients with aggravating factors) rarely (when used in high doses)
– decreased diastolic blood pressure, increased systolic blood pressure, arrhythmia (in including
atrial fibrillation).
From the respiratory system: rarely – cough, local irritation of the respiratory tract, pharyngitis very rarely
paradoxical bronchospasm, laryngospasm.
From the gastrointestinal tract: often – dry mouth is rare – gastrointestinal motility, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea (especially in patients with cystic fibrosis).
From the side of the organ of vision: when the drug enters the eye – mydriasis, increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma, pain in the eyeball, sometimes reversible accommodation and glaucoma are noted during treatment with the drug.
Pain in the eyeball or discomfort, blurred vision, sensation of a halo or colored spots in front of the eyes, combined with conjunctival hyperemia and corneal edema can be symptoms of acute glaucoma. You should use pupil-constricting drops and immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
Allergic reactions: rarely – skin rash, angioedema of the tongue, lips and face, urticaria.
Other: urinary retention, increased sweating, hypokalemia, a feeling of general weakness, myalgia.
Drug Interaction
Concurrent administration of other beta-adrenomimetic agents, systemic anticholinergic drugs and xanthine derivatives (e.g. Theophylline) may enhance the bronchodilatory effect of the drug Ipaterol-native.
Significant attenuation of the bronchodilator effect of the drug is possible with the simultaneous administration of beta-blockers.
Hypokalemia associated with the use of beta-adrenomimetics may be exacerbated by the simultaneous administration of xanthine derivatives, glucocorticosteroids and diuretics. This fact should be given particular attention when treating patients with severe obstructive airways disease.
Hypokalemia may increase the risk of arrhythmias in patients receiving digoxin. In addition, hypoxia may exacerbate the negative effects of hypokalemia on heart rate. In such cases, it is recommended to monitor serum potassium levels.
Caution should be exercised when administering β-adrenergic agents to patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants, as these drugs are capable of enhancing the action of beta-adrenergic agents. Inhalation of agents for general anesthesia of halogenated hydrocarbon anesthetics, such as halothane, trichloroethylene or enflurane, may enhance the effect of beta-adrenergic agents on the cardiovascular system.
Co-administration of Ipaterol-Native with cromoglycic acid and / or glucocorticosteroids increases the effectiveness of therapy.
Overdose
Overdose symptoms are usually associated with the action of fenoterol. Symptoms associated with
over-stimulation of beta-adrenoceptors may occur.
The most likely occurrence of tachycardia, palpitations, tremors, increase in blood pressure, increase in the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure, angina, arrhythmia and feelings of “tides” of blood to the face, feeling of heaviness behind the sternum, increased bronchial obstruction.
Possible symptoms of overdose due to ipratropia bromide (such as dry mouth, poor accommodation) are weak and transient, which is explained by its topical use.
Treatment: sedation is recommended, anxiolytic drugs (tranquilizers), in severe cases – intensive care.
Beta-blockers, preferably selective β-blockers, may be used as a specific antidote. However, patients with bronchial asthma or COPD should consider the possibility of increased bronchial obstruction, which can be lethal under the influence of beta-blockers and carefully selected for their dose.
Storage conditions
In a dry, dark place at a temperature of no higher than 25 ° C. Do not freeze. Keep out of the reach of children.
Expiration
2 Year
Deystvuyuschee substance interferon alfa
-2b, metronidazole, Fenoterol
Dispensing conditions from
pharmacies Prescription
dosage form
dosage form
solution for inhalation
Nativ, Russia