Description
Pharmacological action
Thiazide-like diuretic, antihypertensive agent. It causes a decrease in the tone of smooth muscles of the arteries, a decrease in OPSS, also has moderate saluretic activity, due to impaired reabsorption of sodium, chlorine and water ions in the cortical segment of the Henle loop and the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. The decrease in OPSS is due to several mechanisms: a decrease in the sensitivity of the vascular wall to norepinephrine and angiotensin II by an increase in the synthesis of prostaglandins, possessing vasodilating activity by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into the smooth muscle elements of the vascular wall. In therapeutic doses, virtually no effect on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism.
The antihypertensive effect is manifested only with initially elevated blood pressure, develops by the end of the first week and reaches a maximum after 3 months of systematic administration.
Indications
Arterial hypertension sodium and water retention in chronic heart failure.
Contraindications
Acute cerebrovascular accident, severe renal and / or liver dysfunction, severe diabetes and gout, hypersensitivity to indapamide.
Special instructions
Use with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus (glucose control is necessary, especially in the presence of hypokalemia), gout (possibly an increase in the number of seizures), in patients with a history of allergic reactions to sulfonamide derivatives.
During treatment, it is necessary to control the level of electrolytes in blood plasma (potassium, sodium, calcium).
Composition
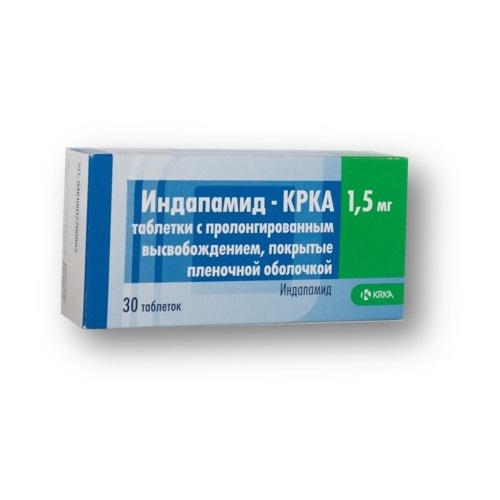
1 tab. contains indapamide 1.5 mg
Dosage and administration
Take orally 2.5 mg 1 time / day (in the morning). If the hypotensive effect is insufficient, after 2 weeks of treatment, the dose is increased to 5-7.5 mg / day.
The maximum daily dose is 10 mg, divided into 2 doses (in the morning).
Side effects of
From the cardiovascular system: often an excessive decrease in blood pressure and related symptoms, rarely arrhythmia, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction and stroke.
From the urinary system: decreased renal function, acute renal failure.
On the part of the respiratory system: often – dry cough, difficulty breathing, rare bronchospasm, rhinorrhea, eosinophilic pneumonia.
From the digestive system: often – nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, taste change, diarrhea or constipation, dry mouth, decreased appetite, cholestatic or cytolytic jaundice, pancreatitis, intestinal edema.
From the central nervous system: often – headache, asthenia, increased uto hypochloremia.
Allergic reactions: skin manifestations.
Dispensing conditions from
pharmacies Prescription
Dosage form
tablets prolong.