Description
Latin name
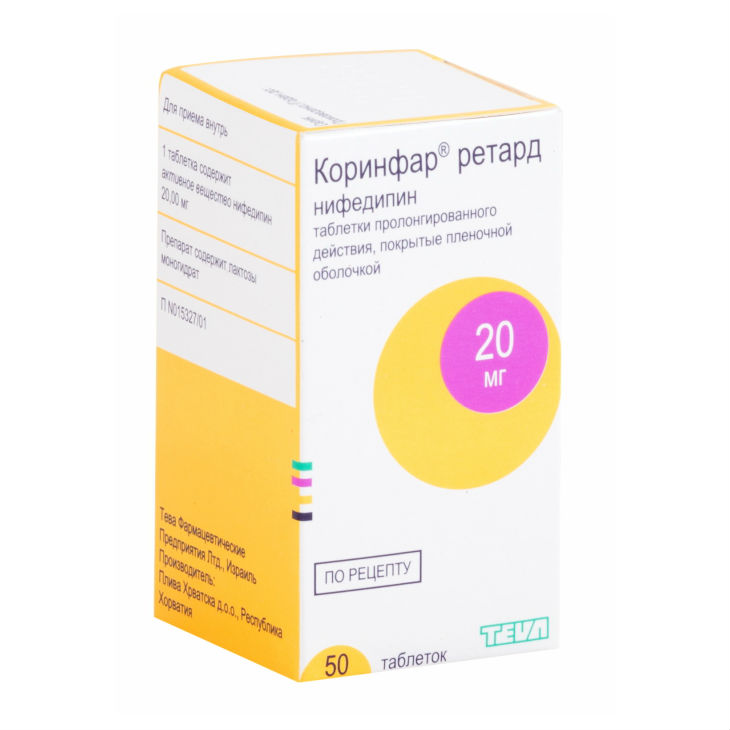
Corinfar retard
Release form
Coated tablets.
Packaging
In a dark glass vial of 50 tablets. In the package 1 bottle.
Pharmacological action
Control – inhibitory proton pump.
Pharmacodynamics
Proton pump inhibitor (H + -K + -ATPase). It blocks the final stage of hydrochloric acid secretion, reducing basal and stimulated secretion, regardless of the nature of the stimulus.
Antisecretory activity. After oral administration of 20 mg of the drug Controlok®, the antisecretory effect occurs after 1 hour and reaches a maximum after 2–4 hours. With iv administration of 80 mg, the antisecretory effect reaches a maximum for 1 hour and lasts 24 hours. In case of duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori, a decrease in gastric secretion increases the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics. Does not affect the motility of the digestive tract. Secretory activity is normalized 3-4 days after the end of the dose.
Compared to other proton pump inhibitors, the Controlok® drug has greater chemical stability at neutral pH, and less potential for interaction with the liver oxidase system, which depends on cytochrome P450. Therefore, the drug Controlok does not interact with many other common drugs.
Pharmacokinetics
Pantoprazole is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Cmax in blood plasma after oral administration is achieved after the first dose of 20 or 40 mg. On average, a Cmax of 1–1.5 μg / ml is achieved after 2–2.5 hours for a dosage of 20 mg and 2.0–3.0 μg / ml after 2.5 hours for a dosage of 40 mg. This indicator remains constant after repeated use of this drug.
Vd is 0.15 l / kg, clearance is 0.1 l / h / kg.
T1 / 2 – 1 h.
Pharmacokinetics are the same after a single or multiple use of the drug.
The binding of pantoprazole to plasma proteins is 98%. Metabolized in the liver. The main route of excretion is through the kidneys (about 80%) in the form of metabolites of pantoprazole, excreted in a small amount with feces. The main metabolite in blood plasma and urine is desmethyl pantoprazole conjugated with sulfate. which plays an important role in the regulation of blood pressure, the drug lowers blood pressure, even in patients with low-arterial hypertension.
A decrease in blood pressure is accompanied by a decrease in total peripheral vascular resistance, a slight increase in cardiac output and the absence of changes or slight changes in heart rate (HR). As a result of enalapril, renal blood flow is crowned, the glomerular filtration rate remains unchanged. However, in patients with initially reduced glomerular filtration, its rate usually increases.
Hydrochlorothiazide is a diuretic and antihypertensive drug that increases renin activity. Although enalapril alone has an antihypertensive effect, even in patients with low-root hypertension, However, when using the recommended doses, the antihypertensive effect and hemodynamic effects persist for 24 hours. Antihypertensive therapy with enalapril leads to significant regression of left ventricular hypertrophy and preservation of systolic function of the left ventricle. Enalapril therapy is accompanied by a beneficial effect on the ratio of lipoprotein fractions and a lack of effect or a beneficial effect on the level of total cholesterol. The use of a combination of enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide leads to a more pronounced decrease in blood pressure compared with monotherapy of each of the drugs separately, and allows you to save the antihypertensive effect of the drug Corenitec for at least 24 hours.
Enalapril reduces the loss of potassium ions caused by the use of hydrochlorothiazide. with insufficiency of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system, chronic intoxications.
Riboflavin (vitamin B 2), as a coenzyme of flavin protein, is involved in the regulation of redox reactions, as well as in the processes of carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism, plays an important role in the synthesis of hemoglobin and in maintaining normal visual function of the eye, the condition of the mucous membranes and skin.
Lipoic acid is involved in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid and -keto acids, in the regulation of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, and plays an important role in the formation of energy in the body. Lipoic acid has a hepatoprotective effect, improves the detoxification function of the liver, and protects against the effects of exo and endotoxins. Reduces peripheral resistance and slightly – myocardial contractility, reduces afterload on the heart and myocardial oxygen demand. Improves coronary blood flow, post-stenotic circulation with atherosclerotic obstruction.
Does not inhibit automatism and myocardial conduction, can cause reflex tachycardia.
Indications
– Stable angina pectoris (exertional angina).
– Angiospastic angina pectoris (Prinzmetal angina, variant angina pectoris).
– Essential arterial hypertension.
Contraindications
– Cardiogenic shock.
– Severe stenosis of the aortic orifice.
– Unstable angina pectoris.
– An acute period of myocardial infarction (during the first 4 weeks).
– Pregnancy.
– Lactation (breastfeeding).
– Hypersensitivity to nifedipine.
Pregnancy and lactation
Corinfar retard is contraindicated in pregnancy.
Nifedipine is excreted in breast milk. Data on the effect of nifedipine on the infant is not enough. Therefore, if you need to use Corinfar retard during lactation, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Composition
1 sustained-release coated tablet contains: nifedipine 20 mg.
Excipients: Lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, macrogol 6000, macrogol 35 000, talc, potato starch, methylhydroxypropyl cellulose, polyvidone K25, microcrystalline cellulose, dyes (E104, E171).
Dosage and administration
Installed individually.
The average dose is 20 mg 2 times / day. With insufficient severity of the clinical effect, a gradual increase in the dose of Corinfar retard to 40 mg 2 times / day is possible.
Maximum daily dose of 80 mg.
The interval between doses should not be less than 4 hours. When prescribing the drug 2 times / day. the recommended intake interval is approximately 12 hours (morning and evening).
Tablets are taken after a meal without chewing and drinking plenty of fluids.
Side effects of
From the cardiovascular system, tachycardia, arrhythmias, palpitations, peripheral edema (ankles, feet, legs), manifestations of excessive vasodilation (asymptomatic decrease in blood pressure, development or aggravation of heart failure, face flushing, skin, feeling hot), a marked decrease in blood pressure (rarely), syncope. In some patients, especially at the beginning of treatment or when the dose is increased, angina attacks may occur, and in rare cases, myocardial infarction develops, which requires drug withdrawal.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness, general weakness, increased fatigue, drowsiness. With prolonged use of the drug in high doses – limb paresthesia, tremor, extrapyramidal (parkinsonian) disorders (ataxia, masky face, shuffling gait, tremor of the hands and fingers, difficulty swallowing), depression.
From the digestive system: dyspepsia (nausea, diarrhea or constipation), dry mouth, flatulence, increased appetite. Rarely – gingival hyperplasia, completely disappearing after drug withdrawal. With prolonged use – impaired liver function (intrahepatic cholestasis, increased transaminase activity).
From the side of the musculoskeletal system: arthritis, myalgia, swelling of the joints.
Allergic reactions: rarely – itching, urticaria, exanthema, autoimmune hepatitis, photodermatitis, anaphylactic reactions, exfoliative dermatitis.
From the hemopoietic organs: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, agranulocytosis.
From the urinary system: increased daily diuresis in the first weeks of admission, impaired renal function (in patients with renal failure).
Other: rarely – visual impairment (i.e., transient blindness with a maximum plasma concentration of nifedipine), gynecomastia (in elderly patients, completely disappearing after withdrawal), galactorrhea, hyperglycemia, pulmonary edema, weight gain.
Drug Interaction
When used with Corinthar Retard with other antihypertensive drugs, as well as with tricyclic antidepressants, there is an increase in the antihypertensive effect of Corinth Retard.
With the simultaneous use of Corinthar retard with nitrates, the effect of Corinthar retard on blood pressure and heart rate is increased.
With the simultaneous use of Corinth, the retard with beta-blockers can cause a more dramatic drop in blood pressure, in addition there have been cases of weakening of cardiac activity.
When Corinthar is used simultaneously with retard and cimetidine (to a lesser extent ranitidine), the effects of Corinthian retard may be enhanced.
With the simultaneous use of Corinthar, the retard with quinidine in some cases decreased the concentration of quinidine in the blood plasma, and after the abolition of Corinthar retard – a sharp increase in the concentration of quinidine in plasma.
With the simultaneous use of Corinth, the retard with digoxin and theophylline in some cases showed changes in the concentration of the latter in blood plasma.
Overdose
Symptoms: loss of consciousness up to coma, drop in blood pressure, tachycardia or bradycardia, hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, hypoxia.
Treatment: artificial vomiting, gastric lavage, symptomatic therapy aimed at maintaining cardiovascular activity.
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored in a dark place.
Expiration
3 years.
Deystvuyuschee substances
nifedipine
terms of sale Uska from
pharmacies Prescription
Dosage form
Dosage form
tablets prolong.
Teva Pharmaceutical Enterprise Co., Ltd., Israel